- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
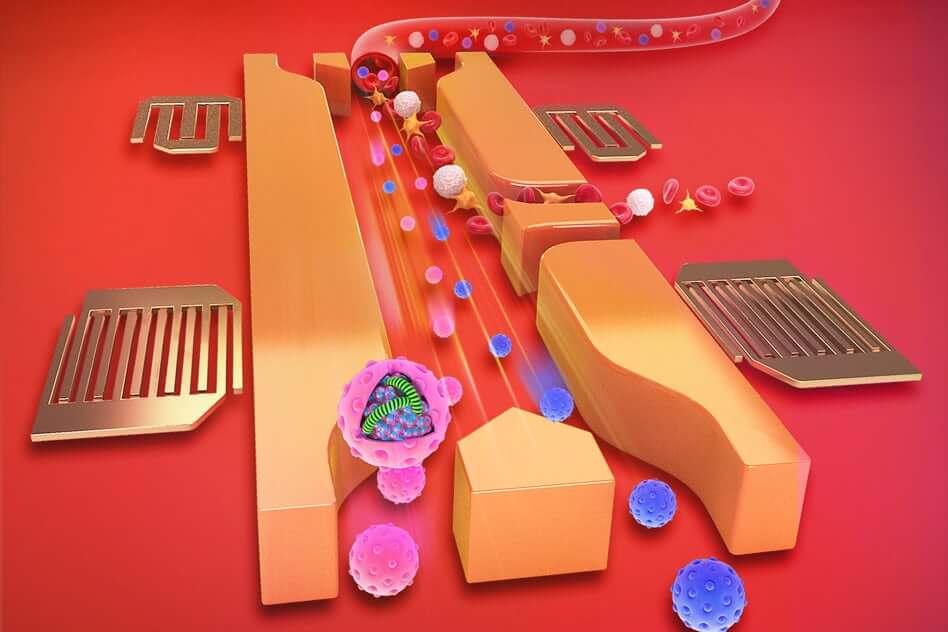
A few years ago, a group of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology announced that it had managed to separate blood cells with the help of sound waves. Now, in cooperation with several other teams of scientists, MIT specialists have perfected their technology, which made it possible to extract exosomes from the blood - microscopic extracellular vesicles with a diameter of 30-100 nanometers. This technology in the future can be an excellent way to quickly diagnose neurodegenerative and oncological diseases in patients.
The new method focuses on isolating exosomes from the blood plasma. Exosomes transport proteins, RNA and lipids inside themselves. You can detect them not only in the blood, but also in cerebrospinal fluid, urine, saliva and even in breast milk. The functions of these vesicles are quite diverse: intercellular communication, participation in the secretion of proteins, facilitating the immune response, but to this day scientists have not been able to study them to the end. But one scientist knows for sure: exosomes can act as the most important markers, signaling that the body has signs of some serious disease.
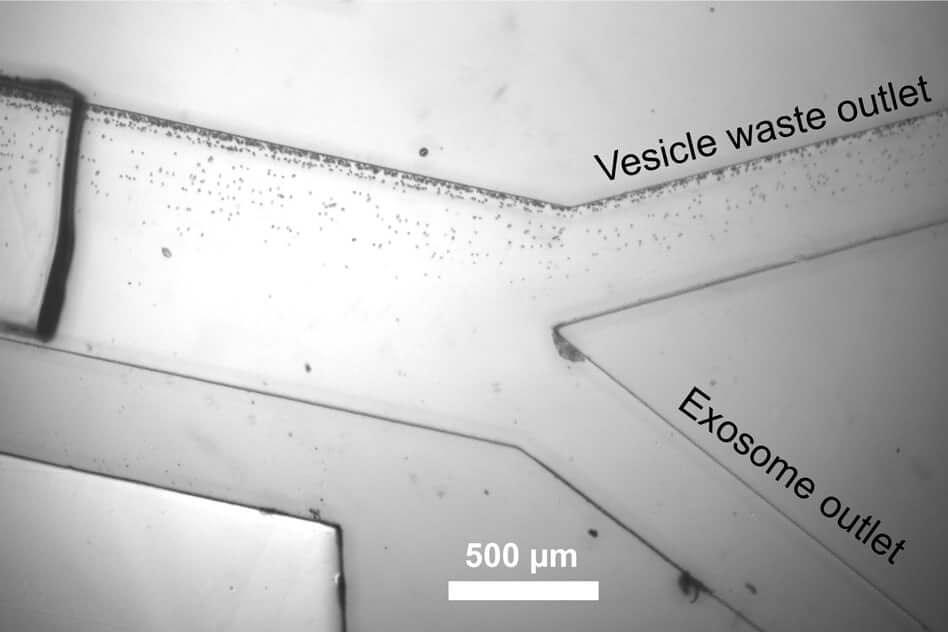
"Exosomes quite often contain special molecules, which are a sign of any deviation from the norm. And if we manage to isolate them from the patient's blood, we can analyze them and find out what they are trying to tell us, "argues the author of the study, Minh Dao.
Earlier, exosomes from the blood sample were taken from scientists for up to 24 hours. It could not do without the costly cumbersome high-speed centrifuge, which not every laboratory can afford. In addition, this very centrifuge could easily damage fragile exosomes in the process of their isolation, which underscored all the efforts of researchers. Sound waves in this regard are much safer and cheaper, and the process of isolating exosomes in this case takes less than 25 minutes for scientists. In the near future, researchers will design and assemble a compact device for isolating exosomes from blood samples that can be used by doctors around the world.
The article is based on materials .
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment